CEX and DEX: How Do Cryptocurrency Exchanges Differ?
Cryptocurrency exchanges serve as the foundation of the digital currency trading ecosystem. They come in two primary types: Centralized Exchanges (CEX) and Decentralized Exchanges (DEX). Each exchange category operates differently and offers varying degrees of control to the users. The purpose of this article is to delve into the characteristics of CEX and DEX, outline their core differences, and enumerate their respective advantages and drawbacks.
Table of contents
- Understanding centralized exchanges (CEX)
- What are decentralized exchanges (DEX)
- Distinctive differences between CEX and DEX
- The pros and cons of CEX
- The pros and cons of DEX
- Conclusion
Understanding Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
Centralized Exchanges (CEX) operate similarly to traditional financial exchanges. They are online platforms where users can buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies, usually against fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies. These exchanges are managed by a central authority that oversees transactions, maintains liquidity, and enforces security measures.
The history of centralized exchanges traces back to the early days of cryptocurrency trading. Platforms like Mt. Gox, established in 2010, were among the pioneers, although the subsequent hacking incidents led to a surge in demand for more secure alternatives. Over the years, CEXs have evolved, implementing advanced security technologies and offering more user-friendly interfaces to attract a wider user base.
Among the most renowned CEX (Centralized Exchange) platforms currently in operation are Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken. Each of these platforms is unique in its own right, offering a vast array of opportunities for cryptocurrency traders.
What are Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) represent a novel approach to cryptocurrency trading. Unlike their centralized counterparts, DEXs eliminate the need for an intermediary, facilitating direct peer-to-peer transactions. Essentially, they are autonomous, open-source platforms where users maintain control over their funds and personal data.
The functioning of DEXs is enabled by innovative technologies like blockchain and smart contracts. Blockchain provides a distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency and security. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, enable the automatic facilitation of transactions once predetermined conditions are met, further reducing the need for intermediaries.
There are several crypto DEX platforms that have gained popularity due to their unique features and emphasis on user control and privacy. Uniswap, for instance, is a leading Ethereum-based DEX that allows for quick trading of any Ethereum ERC-20 token. SushiSwap, a fork of Uniswap, extends the functionalities of its predecessor by incorporating additional features. Balancer operates as an automated portfolio manager and a trading platform, adjusting the portfolio based on predetermined rules. These DEXs are transforming the landscape of cryptocurrency trading by reinforcing user autonomy and ensuring decentralization.
Distinctive Differences Between CEX and DEX
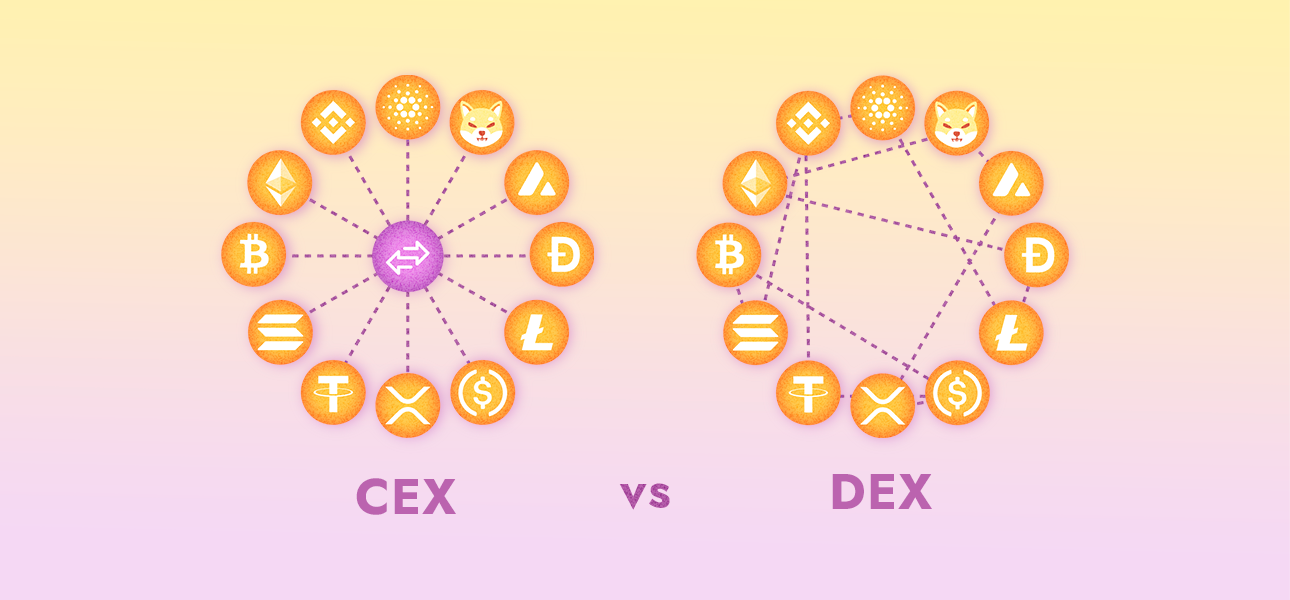
Centralized Exchanges (CEX) and Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) fundamentally differ in how they handle transactions and orders.
CEXs use an order book model where they match buy and sell orders from users within their system. This traditional model, used by platforms like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken, can provide fast transaction times and high liquidity. These exchanges are generally known for their user-friendly interfaces and robust customer support.
On the other hand, DEXs operate through smart contracts on a blockchain. Instead of matching orders, these exchanges use liquidity pools. Users can directly transact with these pools, swapping tokens on demand. DEXs also offer access to a broader range of tokens, particularly those from newer, less-established projects.
While the technical backbone of DEXs may seem complex, they've been making strides in improving user experience and interface. However, it's essential to note that DEXs typically require a greater degree of self-reliance and understanding of blockchain technology from users compared to CEXs.
In summary, while CEXs offer a user-friendly and supported experience, DEXs offer a broader range of tokens and a decentralized trading environment.
The Pros and Cons of CEX
Advantages of CEX:
- CEXs offer intuitive interfaces and customer support, making them accessible for beginners.
- CEXs typically have high trading volumes which lead to high liquidity.
- Many CEXs use advanced security measures to protect user funds and information.
- CEXs often support trading with fiat currencies, making it easier for users to cash in and out.
Disadvantages of crypto CEX:
- Users don't have full control over their funds on a CEX, which can be a security risk.
- Personal identification is often required for KYC regulations, potentially compromising user privacy.
- Being centralized structures, CEXs present an attractive target for hackers.
The Pros and Cons of DEX
Advantages of crypto DEX:
- DEXs allow users to retain full control over their funds, reducing reliance on third parties.
- With less stringent or complete absence of KYC requirements, DEXs can offer more privacy than their centralized counterparts.
- DEXs often support a wider range of tokens, including those from new or niche projects.
Disadvantages of DEX:
- DEXs can be less user-friendly, often requiring a better understanding of blockchain technology.
- Compared to CEXs, DEXs may have lower liquidity, which could impact the speed and price of trades.
- As DEXs rely on smart contracts, any bugs in the contract code can pose potential risks.
Conclusion
Both CEX and DEX have crucial roles in the cryptocurrency exchange environment, each offering distinct benefits and encountering specific challenges. Choosing between these platforms typically depends on individual user preferences and requirements, including factors such as security, control of funds, privacy, and user-friendliness. As the cryptocurrency industry continues to evolve, it is likely that both types of exchanges will coexist, with users selecting the one that best fits their specific needs.
► Sabai Academy — a place where studying blockchain, crypto, fractional ownership, and real estate investments becomes a catalyst for capital growth!
Sabai Academy
Join our FREE courses and get REWARDS IN CRYPTO!
Related Articles
Blockchain Technology Scopes of Use

What are DApps, and How Do They Work?

